Indian police have
launched a hunt for a Sikh preacher who has revived talk of an
independent Sikh homeland and stoked fears of a return to
violence that killed tens of thousands of people in 1980s and
early 1990s.
Police in the northwestern state of Punjab, where Sikhs are
in the majority, said they had arrested 114 supporters of the
preacher, Amritpal Singh, 29, and claimed seizing 10 guns and 430 rounds
of ammunition and other equipment.
Police said they had stepped up their presence and suspended
mobile internet services to prevent unrest.
Police have accused Singh and his supporters of attempted
murder, obstruction of law enforcement and creating disharmony
and said he had been on the run since Saturday when officers
tried to block his motorcade and arrest him.
Top Punjab police officer Sukhchain Gill told the Reuters news agency that
Singh had set up a militia called Anandpur Khalsa Fauj [or Anandpur Army of the Pure].
Its
logos were found on the gate of his house and on the rifles and
bullet-proof jackets recovered there, Gill said.
READ MORE: Dozens arrested as Indian police hunt for Sikh separatist leader
‘Still slaves’
Singh’s father, Tarsem Singh, told reporters the hunt for
his son was a “conspiracy”, adding that Amritpal was only
working to fight drug addiction.
At a rally in September, Singh said in a speech that every
drop of his blood was dedicated to “freedom for the community”.
“We all are still slaves … We have to fight for freedom,”
Singh said in the home village of Jarnail Singh Bhindranwale,
the Sikh insurgent leader killed in a 1984 Indian army
operation.
Singh has said striving for a separate country, that Sikhs
call Khalistan, was not an anti-democratic and should not be
taboo.
Sikh groups complaining of unfair treatment on the part
of the central government began agitating for a separate
homeland in the 1970s.
India’s then prime minister, Indira Gandhi, sent the
military into the Golden Temple, the holiest shrine for Sikhs,
in 1984 to root out Bhindranwale and his supporters in a bloody
episode that infuriated Sikhs around the world.
A few months later, Gandhi was assassinated by her Sikh
bodyguards at her home in Delhi.
Her assassination sparked anti-Sikh riots across India in which thousands of Sikhs were killed by Hindu mobs, including 2,733 in capital New Delhi alone.
While the Sikh insurgency was suppressed in the 1990s,
authorities have been wary of any revival of agitation, with a
particular focus on small groups of Sikhs in Canada, Britain,
the United States and Australia, who support the separatist
demand and occasionally stage protests outside Indian embassies.
The Indian Foreign Ministry has complained about the
protests and sought better security for its missions.
READ MORE:
Sikh Indian player faces online abuse over dropped catch in Pakistan match
‘Direct link’
While some Sikh community leaders say the demand for a
separate Khalistan has little support in Punjab, some security
officials warn that trouble could again brew if activists like
Singh are not stopped.
Media reported that Singh had spent a decade in Dubai
working in his family’s transport business before returning to
India in September and taking over the leadership of a Sikh
group Waris Punjab De, or heirs of Punjab.
Singh had become popular through social media during drawn
protests in 2020-21 by thousands of farmers from Punjab, many of
them Sikh, against agricultural reforms.
Another Indian security officer said while Singh had only a
few tens of thousands of supporters in India, he had an extensive
social media reach, especially abroad, which the officer linked
to the embassy protests.
“Surely what’s going on at missions abroad is a reaction to
the operation against him. There is a direct link,” said the
officer, who declined to be identified.
The Sikh insurgency of the 1980s and 1990s killed some
30,000 people.
Sikh rebels were blamed for the 1985 bombing of an Air India Boeing 747 flying from Canada to India, in which all 329 people on board were killed.
READ MORE:
Farmer protests continue as India fumes over Canadian ‘interference’

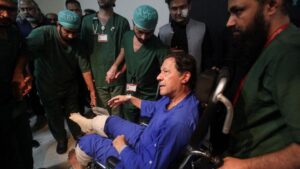
![On the run since last week, Amritpal Singh [centre] maintains striving for a separate country, that Sikhs call Khalistan, was not an anti-democratic and should not be taboo.](https://www.infonewsall.com/storage/152363_ind20230303_1679446832882.jpg)
















































Be First to Comment