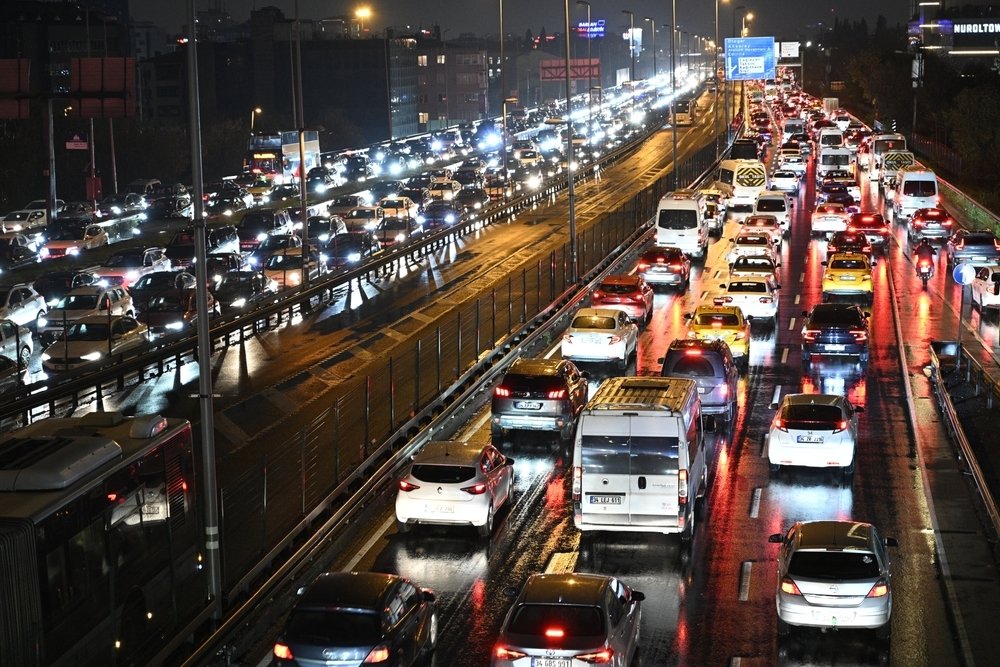
Researchers from Istanbul Technical University (ITU), led by professor Levent Kuzu, have developed an innovative method using AI to calculate vehicle emissions through traffic camera images.
Supported by the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Türkiye (TÜBİTAK), the project aims to improve air quality predictions by combining AI with computational fluid dynamics, enabling real-time tracking of vehicle-related pollution in urban areas.
The new method leverages deep learning algorithms to analyze traffic camera footage, classifying vehicles and determining their density. This data is then used to generate high-resolution air quality maps, providing more accurate predictions of pollution levels in cities.
By tracking emissions from vehicles, which are a major contributor to urban air pollution, the system allows for more precise assessments of environmental conditions.
Kuzu, who teaches in ITU’s Environmental Engineering Department, explained that traffic is one of the primary sources of air pollution, alongside industrial activities and residential heating.
He noted that pollutants such as carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides and particulate matter are typically emitted from vehicle combustion processes. Traditional methods of monitoring air quality often rely on general or average data, which limits the accuracy of predictions for specific urban regions. The new AI-based method overcomes this by using detailed, real-time data for more accurate emission forecasting.
The system operates in three phases. First, deep learning algorithms analyze traffic camera images to classify vehicles and estimate their speeds. Second, emission factors specific to each vehicle type are applied to calculate the pollution generated by each group. Finally, computational fluid dynamics models, combined with meteorological data, help determine the impact of these emissions on surrounding air quality.
This allows the model to predict pollutant concentrations at specific locations without the need for fixed air quality monitoring stations.
During pilot testing in Istanbul, the team used traffic cameras to validate the method’s effectiveness. In one case, the model predicted vehicle presence with over 95% accuracy and successfully calculated emissions and pollution concentrations in real-time.
The results were compared with data from a nearby air quality station at Yıldız Technical University, confirming the model’s accuracy and reliability.
This new approach offers a valuable tool for urban planners and authorities to make informed decisions about air quality management.
Kuzu emphasized that understanding the sources of air pollution, particularly traffic-related emissions, is crucial for improving urban air quality. With this AI-driven method, cities can more effectively monitor and manage pollution, ultimately contributing to cleaner, healthier environments.

















































Be First to Comment